- HOME
- About Us
- President’s Message
- Philosophy
- Charter of Corporate Behavior
- Company Profile
- Location List
- Company History
- Award history
- Directors
- Professional Qualified Staff
- Patent acquisition · NETIS registration technology
- General Employer Action Plan
- Promotion of working-style reform hatarakikata
- Quality / Environment Policy
- 50th Anniversary Commemorative Event
- Privacy Policy
- Basic Information Security Policy
- Sectors & Services
- Bridges
- Urban Facility Design
- Roads
- Traffic
- Urban & Regional Planning
- Environment
- Aesthetic Design
- Rivers
- Erosion Control
- Geological Disaster Prevention
- Tunnel
- Ports
- ICT
- Management
- Energy
- Technology Development
- Overseas
-

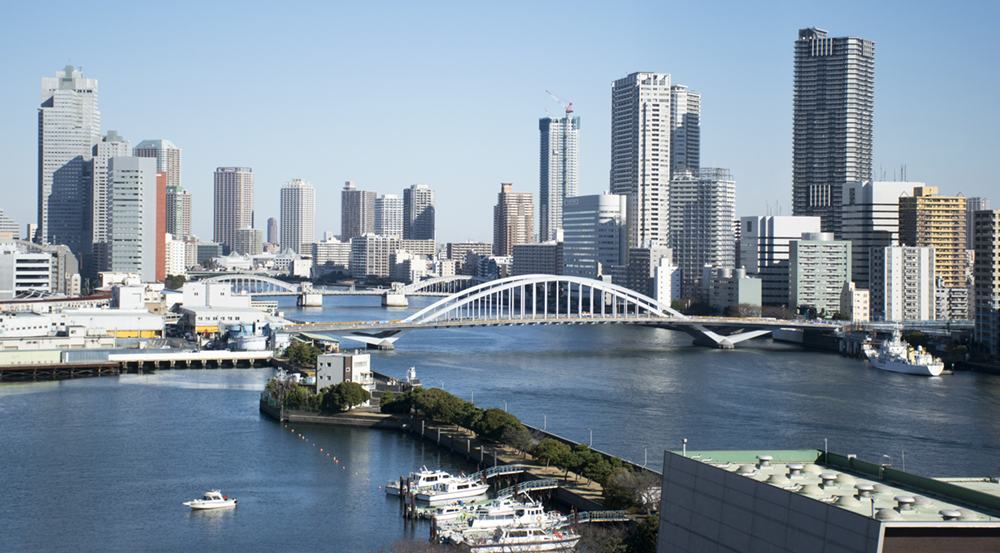
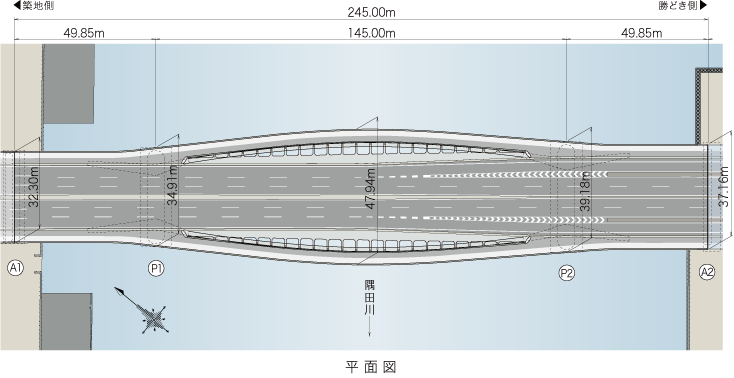
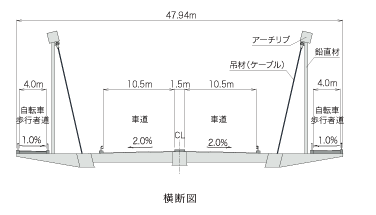
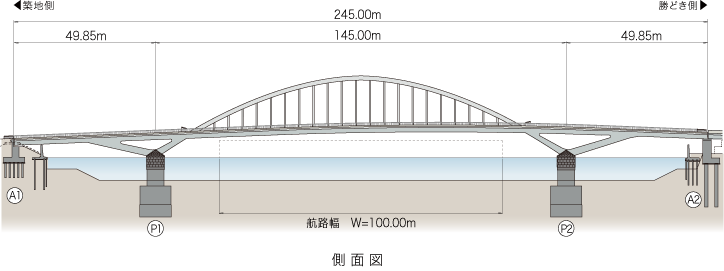
Bridge
We develop bridges that are seen by many people and become local landmarks, with designs that are suitable for the site, structures that are easy to maintain and manage, and excellent lifecycle costs.
Urban Facility Design
We provide comprehensive technical services that can be adapted to satisfy diverse needs and complex construction requirements.
Roads
We provide planning, design, and measures, which utilize our comprehensive consulting prowess, for all kinds of road related things, like bridges, tunnels, underground structures, and roads themselves. We also provide environmental, landscape, and soil quality analyses.
Traffic
The smooth interaction of people and things greatly influences local economies. We strive to create transportation networks that are both efficient and effective, are easy for everyone to use, and contribute to the stimulation of local economies.
Urban & Regional Planning
We strive to comprehensively coordinate strategic, dynamic community and regional development efforts that are based on local characteristics, are committed to consensus building with local residents, and provide comfortable living environments that are adaptable to the needs of future generations.
Environment
We strive for regional development that allows society to coexist with nature, as well to continuously grow without putting a major burden on the environment, by taking on both global scale environmental problems, such as global warming, as well the various ones faced by local areas.
Aesthetic Design
For us, thinking up designs is an intellectual production activity, where we select essential themes, apply logic to them, and end up with reasonable solutions. By utilizing designs that combine necessity with amenity, we are able to realize social infrastructure that is both beautiful and functional.
Rivers
We are engaged with creating social infrastructure that can withstand flooding brought about by climate change or earthquakes, to better ensure the safety and security of people's life. We also carry out operations and management (O&M) and renewal of social capital and building rivers with a view toward better river ecology.
Erosion Control
Japan's terrain is about 70% mountains. What's more, between heavy rain, earthquakes and volcanoes, the environment is perfect for landslide disasters. So to better help protect the lives and property of local residents, we offer a rich line of services to create safe living spaces that offer peace of mind.
Geological Disaster Prevention
We deal with solving any geologic or ground issues in the planning, layout and building roads, bridges, tunnels, rivers and erosion control installations. We can also carry out activities to help with O&M, survey and inspection of existing structures, ground and slope disaster prevention, and planning for disaster response.
Tunnel
Japan is a mountainous country, so the future demand for tunnels to build safe roads while changing terrain as little as possible is immeasurable. Our company deals with every part of this, from main and facilities planning to inspection, survey and maintenance plans.
Ports
To promote sustainable social growth, we are engaged with the challenges of protecting human life and national interests by creating countermeasures for natural disasters like mega typhoons brought by global warming and earthquake-caused tsunamis, as well as facilities that can compete on the international stage.
Information and Communications Technology
We offer optimal, user-centered solutions particularly within the construction field for activities like computerizing administration, while leveraging our know-how on improving social infrastructure. We are here to support the move towards an IoT based "ubiquitous society."
Management
In order to bring a smile to communities, we are working to deepen our "management" according to social demands.
Energy
We will provide comprehensive technologies for energy management to realize a sustainable "low-carbon, recycling-oriented society" for conservation of the global environment.
Technology Development
We are developing new technologies to develop and build social infrastructure for the future.
Overseas
As a member of the international community, we provide high-quality technical services in all aspects of the development of social infrastructure, nature disaster preparedness measures, research, planning, design, and construction management.
- I R
- Contact us
- JAPANESE